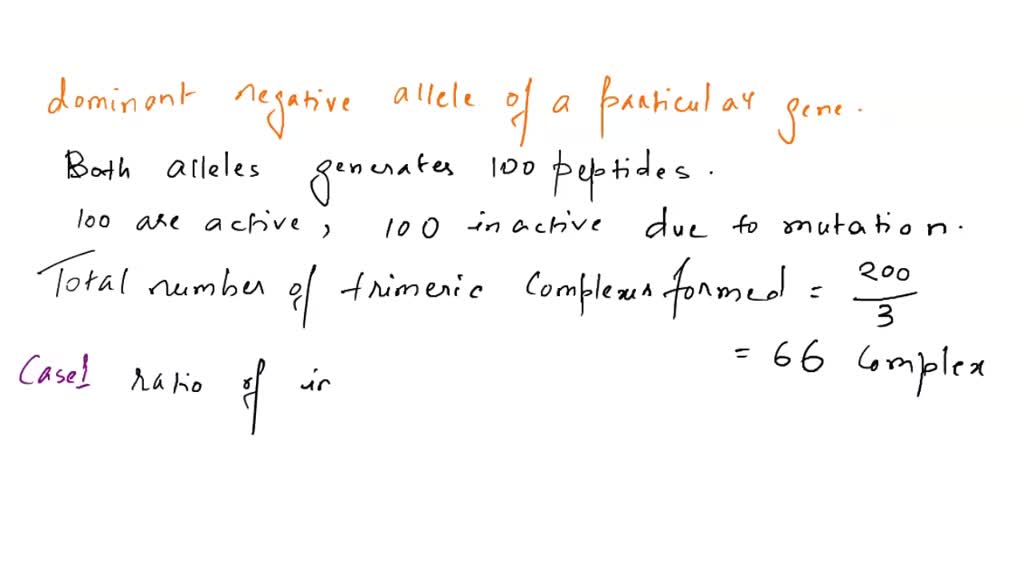Dominant Negative G Proteins Enhance Formation and Purification of Agonist-GPCR-G Protein Complexes for Structure Determination | ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science

Dominant-negative model for inhibition of PS1 activity and stimulation... | Download Scientific Diagram

Dominant and Recessive Compound Heterozygous Mutations in Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex Demonstrate the Role of the Stutter Region in Keratin Intermediate Filament Assembly* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Dominant Negative G Proteins Enhance Formation and Purification of Agonist-GPCR-G Protein Complexes for Structure Determination | ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science
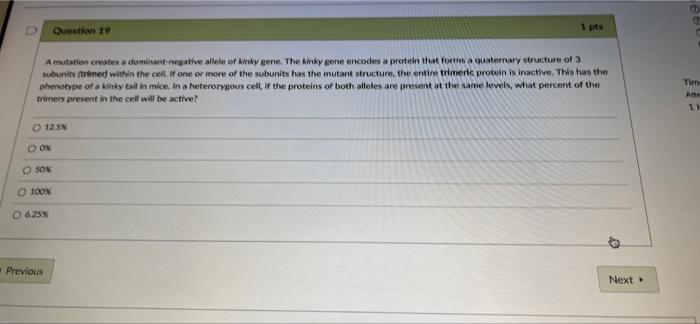
Lecture 4: Mutant Characterization I Mutation types (and molecular nature) Complementation tests Read: 285-293 Fig. 8.28, 8.29,
Lecture 4: Mutant Characterization I Mutation types (and molecular nature) Complementation tests Read: 285-293 Fig. 8.28, 8.29,
Lecture 4: Mutant Characterization I Mutation types (and molecular nature) Complementation tests Read: 285-293 Fig. 8.28, 8.29,

Difference Between Haploinsufficiency and Dominant Negative | Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms

Dominant-Negative Effects of ScpA and ScpB Mutations In Vivo (A) The... | Download Scientific Diagram

SOLVED: What is dominant negative mutation? a) O A mutation that produces polypeptide that will inhibit the activity of the wild type allele: mutation that codes for polypeptide with enhanced function mutation

Mutations in the relay loop region result in dominant‐negative inhibition of myosin II function in Dictyostelium | EMBO reports

Negative-dominance phenomenon with genetic variants of the cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5 - ScienceDirect

Evidence for a dominant-negative mechanism in HARS1-mediated peripheral neuropathy.,The FEBS Journal - X-MOL

haploinsufficiency retrotransposition dominant negative mutations position effect inversion - YouTube